My preferred learning style is kinesthetic and these results were expected. I will still try to study in different ways but copying down diagrams would probably be helpful to me for studying.
Thursday, November 19, 2015
Unit 4 Reflection
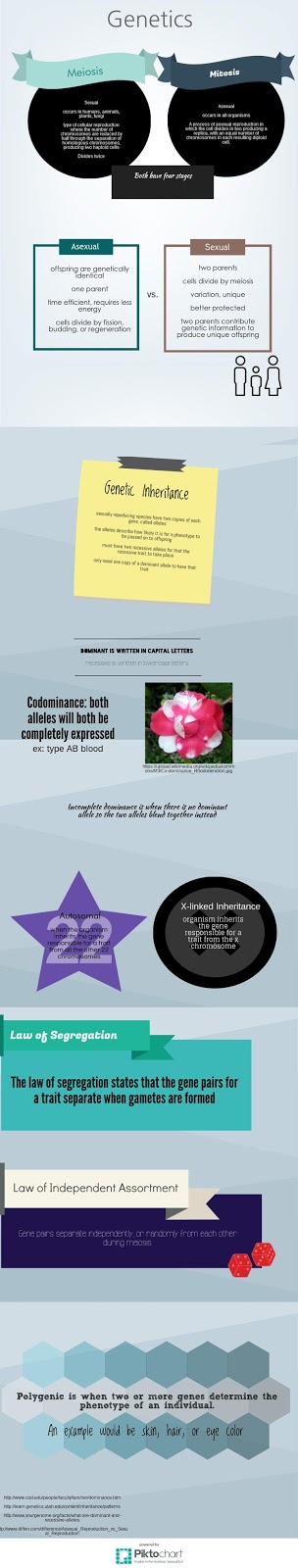
This unit was about the cell cycle, genetics, The cell cycle is a series of steps that take place when a cell duplicates or reproduces. Three reasons for the cell cycle is reproduction, growth and development, and cell and tissue repair. There are two types of reproduction, sexual and asexual. In asexual reproduction , there is only one parent. All the offspring are genetically identical. Some benefits of asexual reproduction is that it's easy, takes a short amount of time, you don't need a mate, and can make lots of offspring. The cost is that there is no genetic variation and is will make it more likely to go extinct if a new pathogen attacks them or their environment changes. The benefits of sexual reproduction is that it creates genetic variation, can allow the parents to raise the young to ensure survival, and create competition for mates, ensuring the best pass on their genes. The cost is that it requires lots of energy and time. It exposes you to parasites and STDs. It could create genetic combinations that are bad. We also learned that all body cells are diploid and all gametes are haploid. In meiosis, there are four stages just like mitosis, but in meiosis it divides twice. Homozygous is having two of the same allele while heterozygous is having two different alleles. The law of segregation states that the gene pairs for a trait separate when gametes are formed. The law of independent assortment states that the gene pairs separate randomly from each other during meiosis. Autosomal inheritance is when an organism inherits or gets the gene responsible for a trait from all the other 22 chromosomes which are called autosomes. X-linked inheritance is when an organism inherits, or gets, the gene responsible for a trait from the x chromosome. The most difficult thing to understand in this unit is probably crosses. A dihybrid cross is comparing two genes at the same time and the phenotypic ration is 9:3:3:1.
My preferred learning style is kinesthetic and these results were expected. I will still try to study in different ways but copying down diagrams would probably be helpful to me for studying.
My preferred learning style is kinesthetic and these results were expected. I will still try to study in different ways but copying down diagrams would probably be helpful to me for studying.
Monday, November 16, 2015
Coin Sex Lab
In this lab, we flipped coins to simulate the randomness of alleles. The coins were the genes and the sides were like the different alleles. This simulated the process of meiosis and the recombination of these genes. This showed how random it is. There is a very low chance of getting homozygous genotypes in dihybrid crosses. You can see what the probability of something is, but you'll never know what you will actually get. The coin flipping was also gene segregation and the results after flipping was the recombination. In part two we tested autosomal dominance, the ones on the 22 chromosomes. In part 3 we did an experiment on x-linked recessive traits, which in this experiment we used the allele for colorblindness. X-linked inheritance is the trait you get from the x chromosome. Monohybrid was the ones we did using only one gene. We also found the different probabilities for either heterozygous or homozygous phenotypes. For the first experiment, the females were homozygous x. Males were heterozygous. Our last experiment was dihybrid, and tested for the different colors of hair and eyes. It was wither brown or blonde hair and brown or blue eyes. This experiment showed that neither trait affected the other and it was possible to get lots of different combinations. This relates to our life because it shows what the probability is of getting certain traits for our offspring.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)